Blockchain is one of the most talked-about technologies in the world today, yet for many beginners, it still feels complicated. You may hear phrases like decentralized networks, peer-to-peer transactions, or immutable ledgers and wonder what any of that actually means.
But the truth is simple: blockchain is just a secure digital system that records and verifies information without relying on a central authority. And this single idea is reshaping finance, the internet, and how people interact online.
Today, everything from digital payments to tokenized assets (including our projects which is IPO Genie) is powered by blockchain because it is transparent, trust-based, and extremely difficult to manipulate.
In this guide, we’ll break down blockchain explained from its meaning to how it works, using clear, easy language. By the end, you’ll fully understand what blockchain is and how it works, why the world is shifting toward it, and why investors and Web3 users should pay attention.
What Is Blockchain? (Simple Explanation)
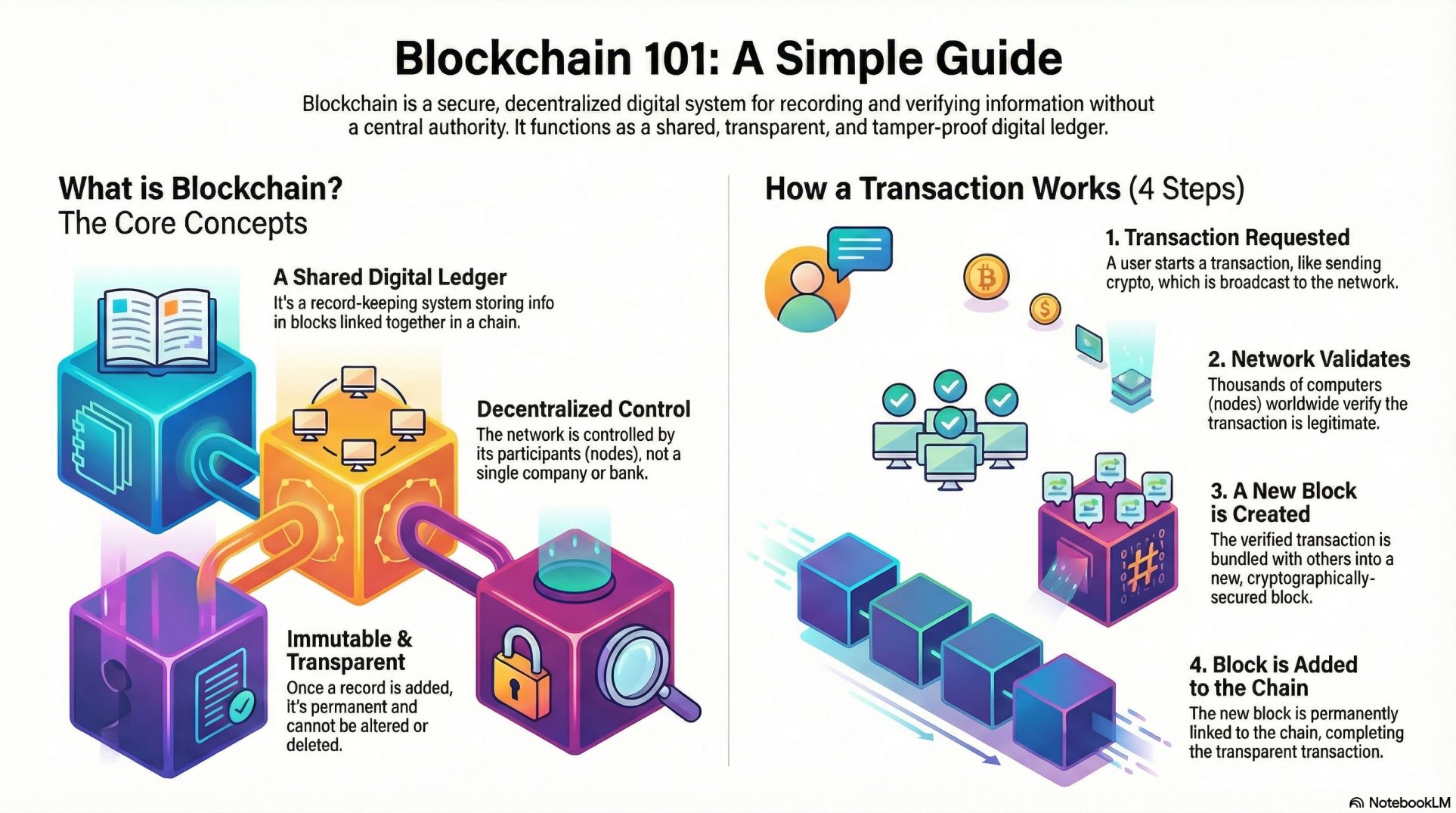
In simple terms, blockchain is a digital record-keeping system that stores information in blocks that are linked together in a chain. So, every block contains data (like transactions or digital records), a timestamp, and a unique code called a hash. Thus, the hash of the previous block, linking them together
Because each block is connected, and each piece of information is verified by a network instead of one company, nobody can secretly change or delete data.
In short:
- Blockchain = a shared, secure, transparent digital ledger
- Controlled by a network, not a company
This simple concept is what makes blockchain technology so powerful.
Why Blockchain Matters? The Meaning & Value of Blockchain Technology
Understanding blockchain technology meaning is key to seeing why it's transformative:
- Immutable Records: Once a transaction is written into a block and added to the chain, changing it is extremely hard. Each block links cryptographically to the previous one, so tampering with one block breaks the chain.
- Transparency: All participants in the network can see the ledger. Even if they don’t know who’s behind each address (because of cryptographic keys), they can verify transactions.
- Security via Cryptography: Blockchain uses public-key cryptography. A public key (address) and a private key (secret) secure how transactions are signed and verified.
- Decentralization: No central entity controls the data. The network reaches consensus (agreement) on which transactions are valid, through mechanisms such as Proof of Work or Proof of Stake.
- Programmability: On many blockchains (like Ethereum), you can run “smart contracts”, code that executes automatically when conditions are met.
These features allow use cases far beyond cryptocurrencies: supply chains, voting systems, identity management, decentralized finance (DeFi), and more.
Why Was Blockchain Created?
Blockchain was first introduced in 2008 as the technology behind Bitcoin. Its purpose was clear, to allow people to send money online without banks, to make transactions secure, transparent, and tamper-proof and to create a system that no single person or company controls.
But today, blockchain has grown far beyond cryptocurrency. It powers smart contracts, decentralized applications, Web3 platforms, tokenized assets, digital identity, virtual economies and DeFi (Decentralized Finance)
Therefore, this is also why IPO Genie uses blockchain, we ensure fair, transparent, and secure token distribution for investors.
Blockchain for Beginners
Many beginners ask:
“Why is blockchain such a big deal?”
Here’s the simple answer:
- It gives people control of their money, data, and digital assets.
- It eliminates middlemen who profit from user data.
- It opens doors to investing, earning, and participating in Web3 economies, as our platform IPO Genie provides you right now blockchain services. So, you can invest, earn and participate in our presale and airdrop.
This is why blockchain adoption keeps growing worldwide.
How Does Blockchain Actually Work?
Let’s break down how blockchain works using a simple step-by-step model.
Step 1: A Transaction Is Requested
A transaction can be, sending cryptocurrency, minting an NFT, updating a digital record, and buying tokens in a presale. This transaction is broadcast to the blockchain network.
Step 2: The Network Validates the Transaction
Instead of a bank verifying your transaction, thousands of computers (nodes) around the world verify it using algorithms.
Thus, this is where decentralization comes in, no one entity controls the network. Because third parties control the system and blockchain is secure, transparent and automates smart contracts.
Step 3: A New Block Is Created
Once the transaction is verified. Then, tt is grouped with other verified transactions and a new block is created. So, that block is ready to be added to the chain
Each block has a unique hash, like a fingerprint. So, the next block comes according to the hash numbers.
Step 4: The Block Is Added to the Chain
After validation the new block is linked to the previous block and the chain grows. So, the record becomes permanent and unchangeable
Once added, no one can modify or delete it. This is what makes blockchain so trustworthy.
Step 5: The Transaction Is Complete
Now the transaction is confirmed, recorded, and visible to anyone who wants to check it. So, this creates the transparency, security and accountabilityAnd this is exactly why blockchain is ideal for crypto presales, token launches, and decentralized projects like our top crypto project, IPO Genie.
Types of Blockchains
There are different kinds of blockchains, depending on who can join, who validates, and how they're used:
- Public Blockchains: Open to anyone (e.g., Bitcoin, Ethereum).
- Private Blockchains: Controlled access, only certain participants can join or validate.
- Consortium / Federated Blockchains: Validation is done by a group of pre-selected nodes (organizations).
- Hybrid Blockchains: Combine features of public and private chains.
Each type has trade-offs in decentralization, performance, and governance.
Key Features That Make Blockchain Technology Special
To really explain blockchain technology meaning, here are its defining attributes:
- Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)
Multiple nodes maintain a shared, synchronized ledger, no single point of failure. - Immutability
Cryptographic linking guarantees that once data is recorded, it's extremely difficult to alter. - Consensus Mechanisms
Proof of Work, Proof of Stake, and other protocols ensure that participants agree on the state of the network. - Cryptographic Security
Public/private key pairs and hashing provide security, identity verification, and integrity. - Smart Contracts
These are programmable rules built into the blockchain, enabling automatic execution when conditions are met. - Transparency & Traceability
Because all transactions are recorded and time-stamped, they can be traced. So, it makes blockchain especially useful for auditing, supply chains, and finance.
Why Blockchain Is Transformative - Beyond Cryptocurrencies
While blockchain first gained fame through Bitcoin, its potential goes far beyond digital currencies. Here are some of the most powerful use cases:
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Blockchain enables peer-to-peer lending, automated market makers, and financial instruments without traditional banks.
- Tokenization & Asset Issuance: Projects like IPO Genie rely on blockchain to issue, trade, and settle tokens in a secure, transparent way.
- Supply Chain & Provenance: Companies use blockchain to track goods, verify origins, and enhance trust in logistics.
- Digital Identity: Blockchain-based identity systems offer more control, security, and privacy than centralized systems.
- Voting & Governance: Immutable records make blockchain suitable for transparent voting systems and decentralized governance.
- Healthcare & Records Management: Blockchain can create secure, tamper-resistant health records accessible by authorized parties only.
Blockchain vs Traditional Systems
| Feature | Traditional Systems | Blockchain |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Centralized | Decentralized |
| Security | Single-point failure | Distributed protection |
| Transparency | Low | High |
| Data Ownership | Company-owned | User-owned |
| Speed | Slow cross-border transfers | Instant peer-to-peer |
| Cost | High fees | Low or no fees |
| Trust Model | Middlemen | Open validation |
What Blockchain Means for IPO Genie and Its Users
The IPO Genie team deeply understands the power of blockchain. Here’s why it matters for our platform and community:
- Secure Token Launches: When IPO Genie helps projects launch tokens, blockchain ensures that token issuance is trustworthy and immutable.
- Transparent Fundraising: Blockchain makes it possible to track where funds go, how tokens are distributed, and who holds what. So, all these factors enhance investor trust.
- Smart Contract Automation: We leverage smart contracts to automate aspects of token distribution, vesting, and even refund conditions, reducing human error and risk.
- Decentralized Participation: By building on blockchain, IPO Genie invites a global community to participate in token launches in a peer-to-peer, permissionless way.
- Auditability & Compliance: Blockchain’s transparent ledger allows for easier auditing, compliance checks, and proof of fairness, which matters both for projects and the IPO Genie investor base.
Common Misconceptions - Blockchain for Beginners
Even though blockchain is powerful, many non-technical users have misunderstandings. Here are some clarifications:
- Blockchain ≠ Bitcoin only: While blockchain was introduced by Bitcoin, it's a much broader technology and can be used for any type of data or value, not just cryptocurrency.
- Immutable doesn’t mean flawless: “Immutable” means it’s very hard to change past data, but blockchains still need good design, consensus rules, and security measures.
- Not always fast: Some blockchains (especially public ones) can be slow or expensive when congested.
- Energy concerns: Mechanisms like Proof of Work consume a lot of energy, though newer blockchains and PoS reduce that.
- Governance matters: Who validates the blockchain (and how) can significantly affect decentralisation, security, and control.
Ready to Invest Smarter?
Join the IPO Genie presale and get early access to AI-powered pre-IPO investing.
Buy $IPO NowFrequently Asked Questions
Q: What is blockchain in simple terms?
Blockchain is a shared digital ledger that records transactions across a network of computers. Instead of one company or bank controlling the records, thousands of participants verify and store the data together. It is the foundational technology behind tokenomics and decentralized finance. This makes it transparent, secure, and very difficult to tamper with.
Q: Is blockchain the same as Bitcoin?
No. Bitcoin is a cryptocurrency that runs on a blockchain, but blockchain itself is the underlying technology. Many other cryptocurrencies, applications, and platforms use blockchain technology for purposes beyond digital currency, including supply chain tracking, identity verification, and decentralized finance.
Q: What are the main benefits of blockchain technology?
The core benefits are decentralization, transparency, and security. Because data is distributed across many nodes rather than stored in one place, there is no single point of failure. All transactions are publicly recorded and cryptographically linked, making fraud and unauthorized changes extremely difficult.
Q: Can blockchain be hacked?
While no system is completely immune to attack, blockchain is highly resistant to tampering. To alter a record, an attacker would need to control the majority of the network simultaneously, which is practically infeasible on large public blockchains like Bitcoin or Ethereum. However, vulnerabilities can exist in smart contracts or in how users manage their private keys.